Electrical Salinometer Working Principle
Working Principle of Salinometer
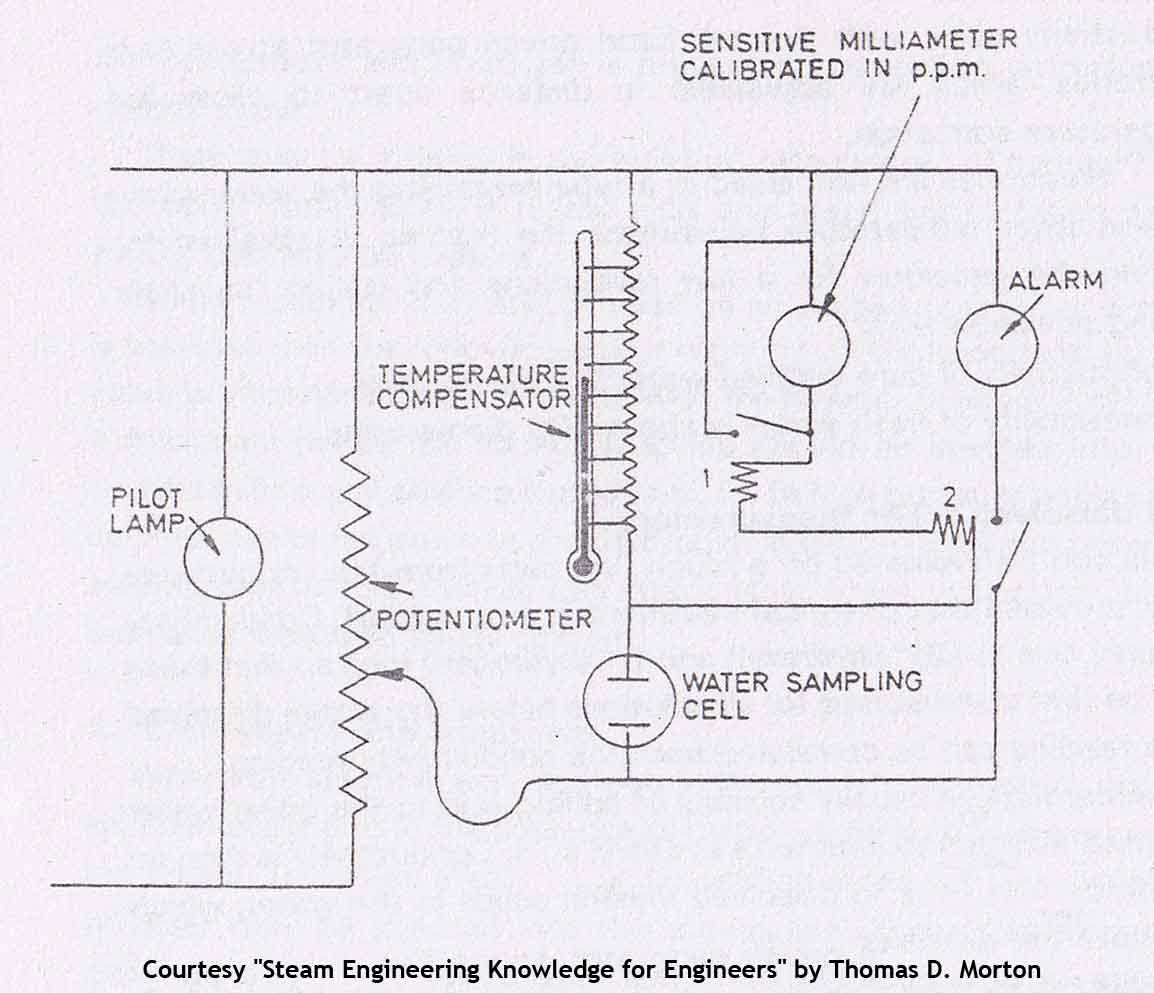
The electrical supply to the salinometer must be DC. The potentiometer is provided to give a fixed standard calibration voltage so that no errors to voltage differences exist.
Pure water is non-conducting so that current flow is an indication of impurities, i.e. the greater the current the greater the impurity in the water. Figure below shows a salinometer usually found with a freshwater generator.
When the impurity content exceeds a fixed value the current is sufficient to operate the relay 2 so giving visual or audible warning by closing the circuit. Continued operation at increased current would cause Relay 1 to short circuit the meter and so protect it.
Water temperature increases conductivity so that temperature compensation is required. A temperature compensating thermometer is a shunt across the meter. Temperature increase causes a rise of mercury level and a cutting out of resistance which allows more current through the shunt and less through the meter. The correct calibration current through the meter is fixed; current variations due to temperature are shunted.
References
“Steam Engineering Knowledge for Engineers” by Thomas D. Morton