Conductors, Semiconductors and Dielectrics
Physical properties of solids, and their electric properties, are determined by the degree of filling of the energy bands rather than by their formation. From this point of view all crystalline bodies can be divided into two different groups.
Conductors
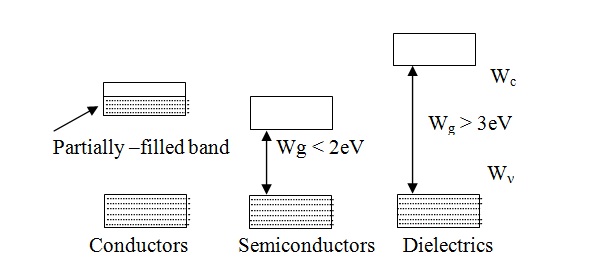
The first group includes substances having a partially filled band in their energy spectrum above the completely filled energy bands. As was mentioned above a partially filled band is observed in alkali metals whose upper band is formed by unfilled atomic levels, and in alkali-earth crystals. All substances belonging to this group are conductors.
Semiconductors and Dielectrics
The second group comprises of substances with absolutely empty bands above completely filled bands. This group also includes crystals with diamond shaped structures such as Silicon, Germanium, gray tin, and Diamond itself. This second group includes semiconductors and dielectrics. The uppermost filled band in these crystals is called valence band and the first empty band above it the conduction band. The upper level of the valence band is called the top of the valence band and is denoted by Wv. The lowest level of the conduction band is called the bottom of conduction band and denoted by Wc.
The division into semiconductors and Dielectrics is quite arbitrary and is determined by the width Wg of the forbidden energy gap separating the completely filled band from the empty band. Substances with a forbidden gap of Wg <2 eV belong to the semiconductor sub-group. Germanium (Wg » 0.7 eV), silicon (Wg» 1.2 eV), gallium arsenide (Wg » 1.5eV), and indium antimonide (Wg » 0.2 eV) are typical semiconductors. Substances for which Wg > 3eV belong to dielectrics. Well known dielectrics include corundum(Wg » 7 eV), diamond (Wg » 5eV). Boron nitride (Wg » 4, 5 eV) and others.
Applications
Conductors like Copper and Aluminum are used to carry electrical current of varying capacities. They are selected on the basis of affordable voltage drop across the ends of the conductor at the specified current.
Semiconductors are used in the manufacture of many electronic devices like Diodes, Bipolar transistors, Field effect transistors, CMOS IC’s etc. Extrinsic semiconductors are doped to make n-type and p-type semiconductors, which are used in the manufacture of these devices.
Dielectrics and Insulators are used where no conductivity is permitted. They are used as Insulating supports for current carrying conductors. Room-temperature superconductor is a material yet to be discovered which would be capable of exhibiting superconducting properties at temperatures above 0° C (273.15 K). This is of course not strictly speaking “room temperature” (20–25° C), however it can be reached very cheaply.
Since the discovery of high-temperature superconductors, several materials have been claimed as being room-temperature superconductors. In every case, independent investigation has quickly proven these claims false. As a result, most condensed matter physicists now welcome with extreme skepticism any further claims of this nature.